Offset printing uses high-speed commercial printing presses to print your data using a process called offset lithography. We have put together this simple guide to explain the basic steps involved.
Offset printing process explained
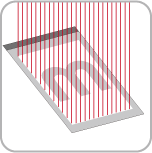
Platemaking
A CTP system takes digital files and images them directly to aluminum plates using laser diodes. This method creates very high quality, accurate printing. The plates are then mounted onto a roller in the printing press, one for each color.
Wetting
Before the plates are exposed to ink, they pass through wet rollers. The dampening solution (water and additives) flows continuously, wetting the entire plate. The plates have been treated to resist water in the places where that color needs to be printed.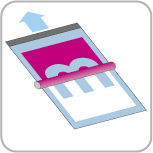
Inking
Next, the ink roller applies oil-based ink to the plate. The thick, oily ink is applied by special vibrating rollers which distribute the ink thinly and evenly. When the ink roller comes into contact with the wet plate, the ink only adheres to the untreated parts of the plate.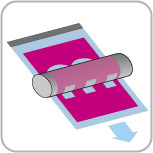
Offsetting
A big rubber roller lifts the ink off the plate, creating a reversed image on the surface of the roller. The roller has some flexibility allowing it to be used with a range of papers, rough, glossy and textured.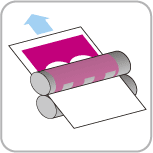
Printing
In the final step individual pieces of paper pass through the rubber rollers (at 5 sheets a second!) and the ink is pressed onto the paper, making a positive image.CMYK inks
Offset printing uses four colored inks - the process colors. The four ink colors are Cyan (C), Magenta (M), Yellow (Y) and Black or Key (K) - more commonly referred to as CMYK. Because the inks used are translucent, they can be overprinted and combined in a variety of different proportions to produce a wide range of colors.
CTP - Computer to plate
Each ink requires its own 'plate'. Your full color digital data is printed with just 4 inks, one on top of the other, so we need to output your file to 4 different plates, one for each color. Each flexible plate created in the imagesetter machine will then be attached to the plate cylinder in the printing press and the corresponding color printed. This color separation and plate making is carried out digitally, directly from your file to the imagesetter using CTP or computer-to-plate technology. Traditionally this was done photographically.
Oil and water don't mix
The basic principle on which it works is that oil and water do not mix. A litho printing plate has non-image areas which absorb water. During printing the plate is kept wet so that the ink, which is inherently greasy, is rejected by the wet areas and adheres to the image areas.
Print speeds of up to 18,000 sheets an hour!
The Press
Commercial presses are huge machines with a separate printing unit for each of the CMYK color inks. The paper is fed through the press at speeds of up to 5 sheets a second (18,000 sheets an hour!) and passes through each ink unit in succession via a complex system of rollers.
Putting the offset into offset printing
During every cycle of the press the ink image is first transferred to a rubber surfaced blanket cylinder and from there to the paper. This indirect method is the 'offset' after which the process is named. The blanket cylinder's flexibility both preserves the delicate plate and conforms to the surface of textured papers.
Finishing
After printing the sheets are taken for finishing. This may include adding gloss or matt laminations to the printed paper but normally means trimming, folding, perforation and binding.
